1. Xenobots

Xenobots are the world's first living robots created from frog stem cells and designed to perform specific tasks such as cleaning up pollution and delivering drugs to specific areas of the body.
2. Synthia

Synthia is the world's first synthetic life form created by a team of scientists at the J. Craig Venter Institute. It was made by synthesizing the genetic code of a bacterium and transplanting it into another bacterium.
3. AIVA

AIVA is an artificial intelligence music composer that uses deep learning algorithms to compose original music in a variety of genres.
4. Amoeba-based Computing
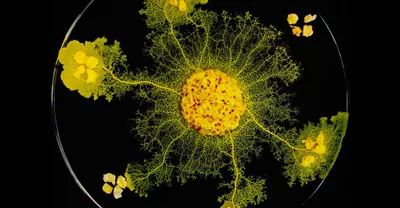
Amoeba-based computing is a new type of computing that uses living amoebas to solve complex problems such as the traveling salesman problem.
5. E. Chromi

E. Chromi is a genetically engineered bacteria that can change color in response to environmental toxins, making it a potential tool for detecting pollution.
6. Spider-goats

Spider-goats are genetically engineered goats that produce spider silk in their milk, which can be used to create super-strong and lightweight materials.
7. Bionic Eyes

Bionic eyes are artificial eyes that can restore partial sight to the blind by converting images into electrical signals that can be sent to the brain.
8. Robotic Fish

Robotic fish are autonomous underwater vehicles that mimic the swimming behavior of real fish, allowing them to explore the ocean without disturbing marine life.
9. Nano-robots
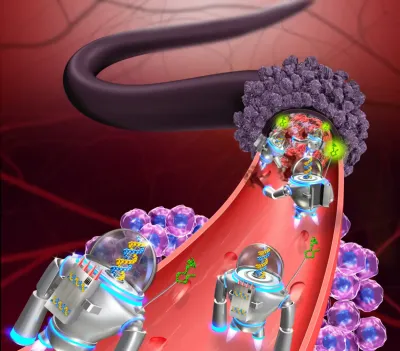
Nano-robots are tiny machines that can be programmed to perform specific tasks such as delivering drugs to cancer cells or repairing damaged tissue.
10. Artificial Womb

An artificial womb is a device that can sustain a fetus outside of the mother's body, potentially revolutionizing the way we approach pregnancy and childbirth.
